Lysario – by Panagiotis Chatzichrisafis
"ούτω γάρ ειδέναι το σύνθετον υπολαμβάνομεν, όταν ειδώμεν εκ τίνων και πόσων εστίν …"
Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”,p. 34 exercise 2.1
Author: Panagiotis21 Sep
In exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.1] we are asked to prove that the inverse of a lower triangular matrix is also lower triangular by using relation [1, p. 23, (2.30)].
read the conclusion >
Hard- und Software Cosimulation mit Visual Micro Lab
Author: Panagiotis6 Sep
Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”,p. 34 exercise 2.5
Author: Panagiotis13 Jun
In exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.5] we are asked to show that
the matrix 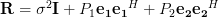 is circulant
when
is circulant
when ![\mathbf{e_i}^H=\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
1 & {e^{-j2\pi f_i } } & {e^{-j2\pi (2f_i) } } & \cdots & {e^{-j2\pi (n - 1)f_i } }
\end{array}} \right], i=1,2](https://lysario.de/wp-content/cache/tex_38ce66bc9234a41f314618cd54d2cfd9.png) .
read the conclusion >
.
read the conclusion >
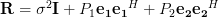 is circulant
when
is circulant
when ![\mathbf{e_i}^H=\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}c}
1 & {e^{-j2\pi f_i } } & {e^{-j2\pi (2f_i) } } & \cdots & {e^{-j2\pi (n - 1)f_i } }
\end{array}} \right], i=1,2](https://lysario.de/wp-content/cache/tex_38ce66bc9234a41f314618cd54d2cfd9.png) .
read the conclusion >
.
read the conclusion >
Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”,p. 34 exercise 2.4
Author: Panagiotis1 Feb
The exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.4] asks to show that if 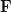 is a full rank
is a full rank 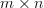 matrix with
matrix with 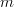 >
> 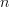 ,
, 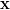 is a
is a 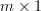 vector, and
vector, and  is an
is an 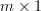 vector, that the effect of the linear transformation
vector, that the effect of the linear transformation
is to project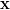 onto the subspace spanned by the columns of
onto the subspace spanned by the columns of 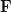 . Specifically, if
. Specifically, if 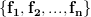 are the columns of
are the columns of 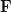 , the exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.4] asks to show that
, the exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.4] asks to show that
Furthermore it is asked why the transform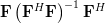 must be idempotent.
read the conclusion >
must be idempotent.
read the conclusion >
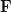 is a full rank
is a full rank 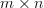 matrix with
matrix with 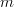 >
> 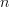 ,
, 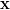 is a
is a 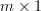 vector, and
vector, and  is an
is an 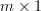 vector, that the effect of the linear transformation
vector, that the effect of the linear transformation
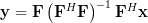 | (1) | ||
is to project
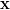 onto the subspace spanned by the columns of
onto the subspace spanned by the columns of 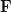 . Specifically, if
. Specifically, if 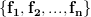 are the columns of
are the columns of 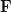 , the exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.4] asks to show that
, the exercise [1, p. 34 exercise 2.4] asks to show that
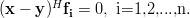 | (2) | ||
Furthermore it is asked why the transform
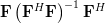 must be idempotent.
read the conclusion >
must be idempotent.
read the conclusion >
Liboff: “Introductory Quantum Mechanics”, 2nd edition p.86 exercise 3.16
Author: Panagiotis2 Jan
The exercise [1, p. 86 ex. 3.16] asks to prove that if the eigenfunctions and eigenvalues of an operator 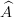 are
are 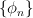 and
and 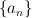 , respectively (
, respectively (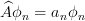 ) then the eigenfunctions of a function
) then the eigenfunctions of a function 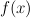 having an expansion of the form:
having an expansion of the form:
will also be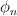 with corresponding eigenvalues
with corresponding eigenvalues 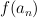 ,
, 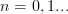 . That is
. That is 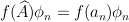 .
read the conclusion >
.
read the conclusion >
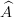 are
are 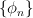 and
and 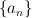 , respectively (
, respectively (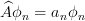 ) then the eigenfunctions of a function
) then the eigenfunctions of a function 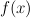 having an expansion of the form:
having an expansion of the form:
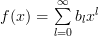 | (1) | ||
will also be
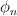 with corresponding eigenvalues
with corresponding eigenvalues 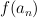 ,
, 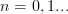 . That is
. That is 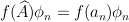 .
read the conclusion >
.
read the conclusion >