Lysario – by Panagiotis Chatzichrisafis
"ούτω γάρ ειδέναι το σύνθετον υπολαμβάνομεν, όταν ειδώμεν εκ τίνων και πόσων εστίν …"
Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”,p. 35 exercise 2.17
Author: Panagiotis16 Aug
In [1, p. 35 exercise 2.17] we are asked to verify the alternative expression [1, p. 33 (2.77)] for a hermitian function.
Solution: The standard expression of the hermitian function is given by [1, p. 32 (2.73)] :
The alternative expression [1, p. 33 (2.77)] is given by
with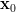 given by [1, p. 33 (2.75)] which is reproduced here:
given by [1, p. 33 (2.75)] which is reproduced here:
Using equation 4 we can compute using the matrix property of invertible matrices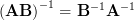
Using (5) in (3) considering the matrix property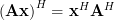 will result in:
will result in:
The last result (6) verifies the alternative expression (3) to be equivalent to the standard hermitian function (1). QED.
[1] Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 0-13-598582-X.
Solution: The standard expression of the hermitian function is given by [1, p. 32 (2.73)] :
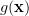 |  | 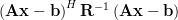 | (1) |
 | 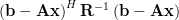 | (2) |
The alternative expression [1, p. 33 (2.77)] is given by
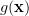 |  | 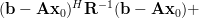 | |
 | 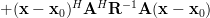 | (3) |
with
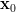 given by [1, p. 33 (2.75)] which is reproduced here:
given by [1, p. 33 (2.75)] which is reproduced here:
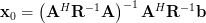 | (4) | ||
Using equation 4 we can compute using the matrix property of invertible matrices
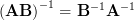
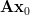 |  | 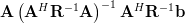 | |
 | 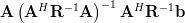 | ||
 | 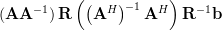 | ||
 | 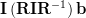 | ||
 | 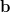 | (5) |
Using (5) in (3) considering the matrix property
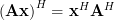 will result in:
will result in:
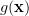 |  | 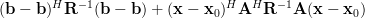 | |
 | 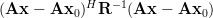 | ||
 | 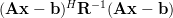 | (6) |
The last result (6) verifies the alternative expression (3) to be equivalent to the standard hermitian function (1). QED.
[1] Steven M. Kay: “Modern Spectral Estimation – Theory and Applications”, Prentice Hall, ISBN: 0-13-598582-X.
Leave a reply